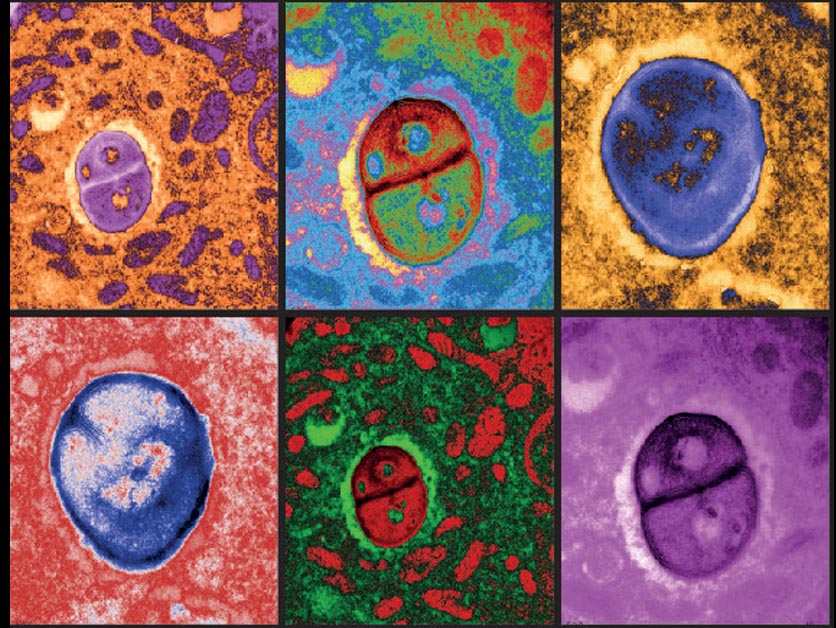
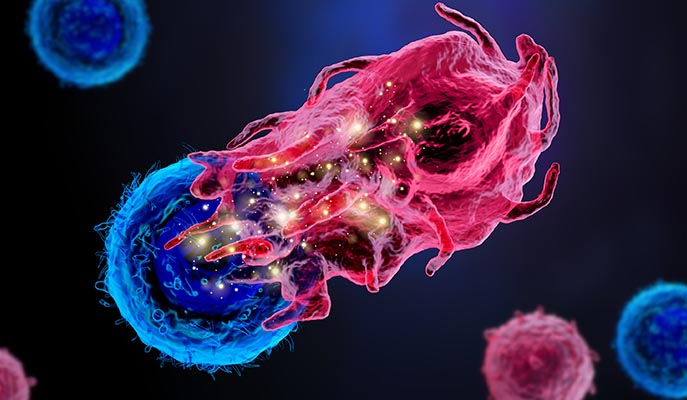
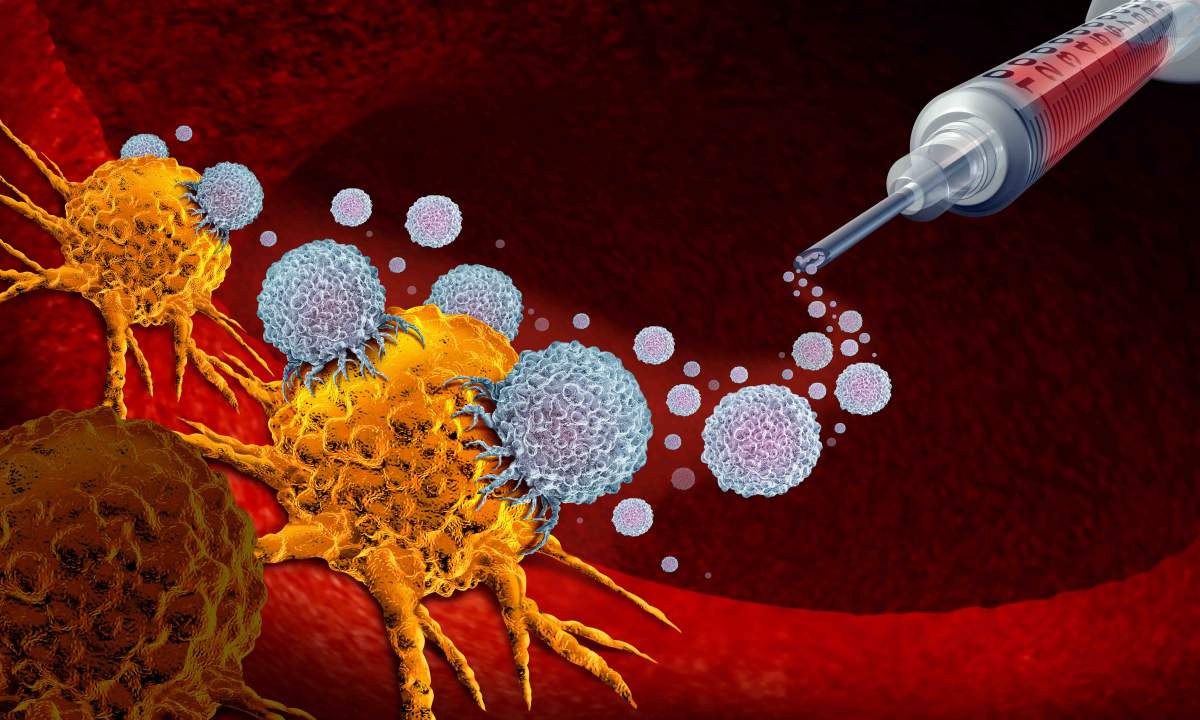
In an innovative study published in Nature Medicine, researchers have taken an important step towards developing a promising treatment strategy for glioblastoma, a challenging brain cancer type. This study merges two novel strategies. The dual-action approach begins with the intratumoral delivery of a virus, DNX-2401, specifically designed to invade and break down the tumor cells from within. Next, a checkpoint inhibitor, pembrolizumab, is introduced intravenously to reignite the immune system, reinforcing the body's own defenses against the cancer. The phase I/II study, involving 49 patients, demonstrated impressive safety and tolerability. While the primary efficacy tumor reduction goal wasn't entirely met, the survival outcomes signal a significant advancement, with a 12-month survival rate of 52.7%, surpassing the 20% control rate substantially. Furthermore, more than half of the patients showed clinical benefits with disease stability or better, and three patients remarkably survived for 45, 48, and 60 months respectively. This innovative combination therapy brings a glimmer of hope for those battling glioblastoma, underscoring the potential for further developments in this exciting field of research.